25 ++ yield point graph 318529-Yield point graph
When a yield point is not easily defined based on the shape of the stressstrain curve an offset yield point is arbitrarily defined The value for this is commonly set at 01 or 02% plasticA stressstrain graph gives us many mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation during load It also helps in fabrication Whether you are looking to perform extrusion, rolling, bending or some other operation, the values stemming from this graph will help you to determine the forces necessary to induce plastic deformationYield Strength Graph The point at which the material transforms from elastic to plastic is known as the yield point The magnitude of the stress at which the transition from elastic to plastic occurs is known as the yield strength Yield strength is a constant that represents the maximum limit of
Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
Yield point graph
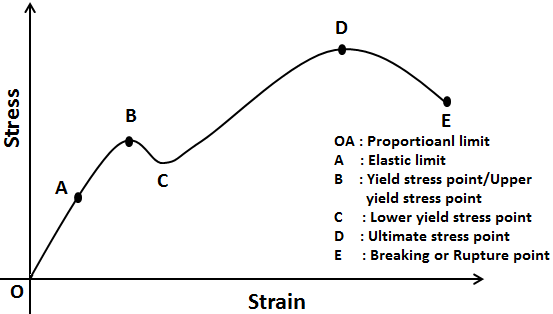
Yield point graph-The StressStrain Graph Yield Strength Whether a material is pliant or stubborn can be discerned by something called its yield strength The point at which a material ceases to be elastic and becomes permanently plastic, the point at which it yields, is called its yield pointIt is indicated in Figure 5 as Point (D) Yield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis


Solved 2 Explain The Engineering Stress And Strain Relat Chegg Com
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsThe yield point, alternatively called the elastic limit, marks the end of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviour When stresses less than the yield point are removed, the material returns to its original shape For many materials that do not have a welldefined yield point, a quantity called yield strength is substituted Yield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percentIn materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and
The CMT yield values are read from the yield curve at fixed maturities, currently 1, 2, 3 and 6 months and 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, , and 30 years This method provides a yield for a 10 year maturity, for example, even if no outstanding security has exactly 10 years remaining to maturityDifferent values may be obtained if tangents are drawn at different points Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield pointThis point is known as the yield point A further increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress The stressstrain behavior of a polymer greatly depends on the temperature At very low temperature well below the glass transition temperature, brittle failure is observed as a break at low strain rate at the stress maximum
Displacement curve The yield point is determined as the intersection of those two lines (K α and K β) as can be seen in Figure 1b (c) Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) In this case the yield point is obtained by multiplying the value of the displacement at 40% of the peak load by a factor of 125When a yield point is not easily defined based on the shape of the stressstrain curve an offset yield point is arbitrarily defined The value for this is commonly set at 01 or 02% plasticThe yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube


In The Simplest Way Explain The Lower Yield Point In The Stress Strain Graph For Steel What Would You Observe Quora
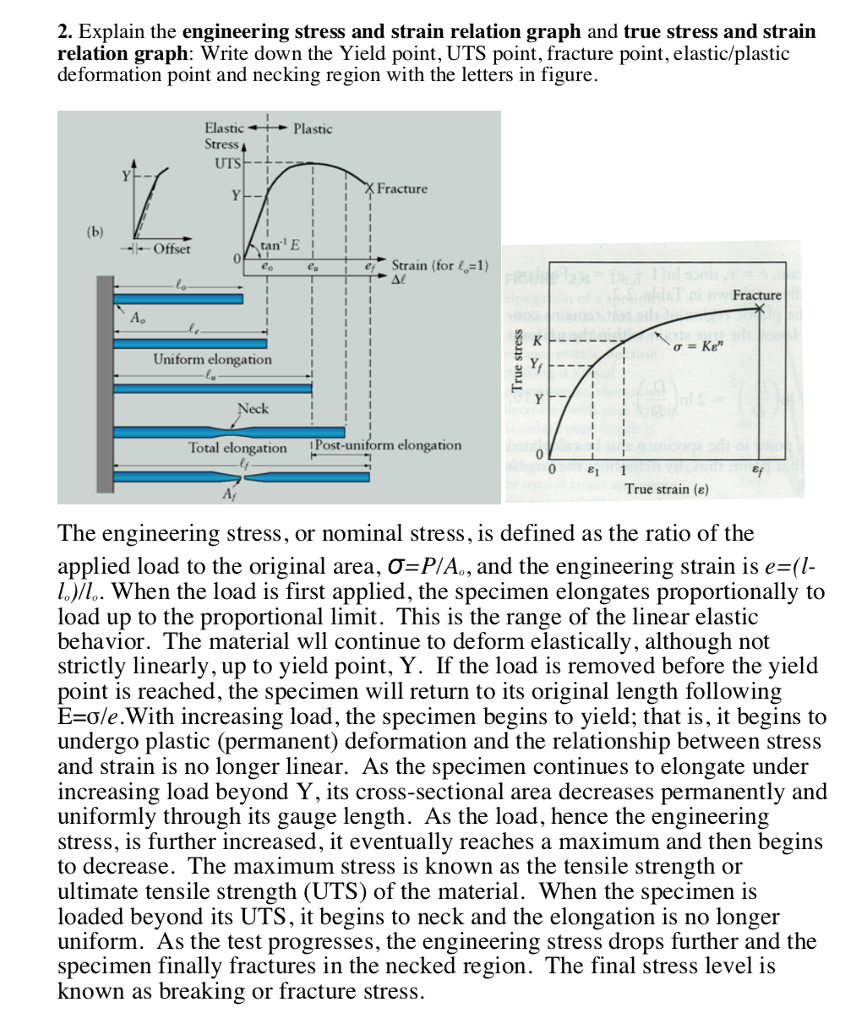
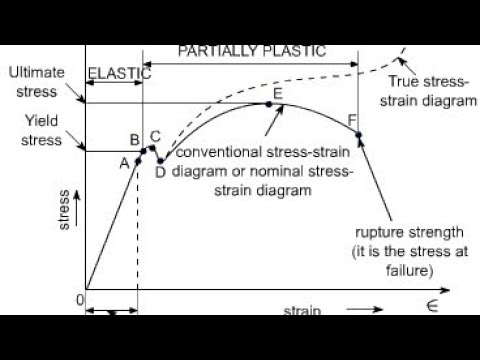
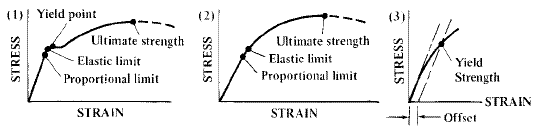
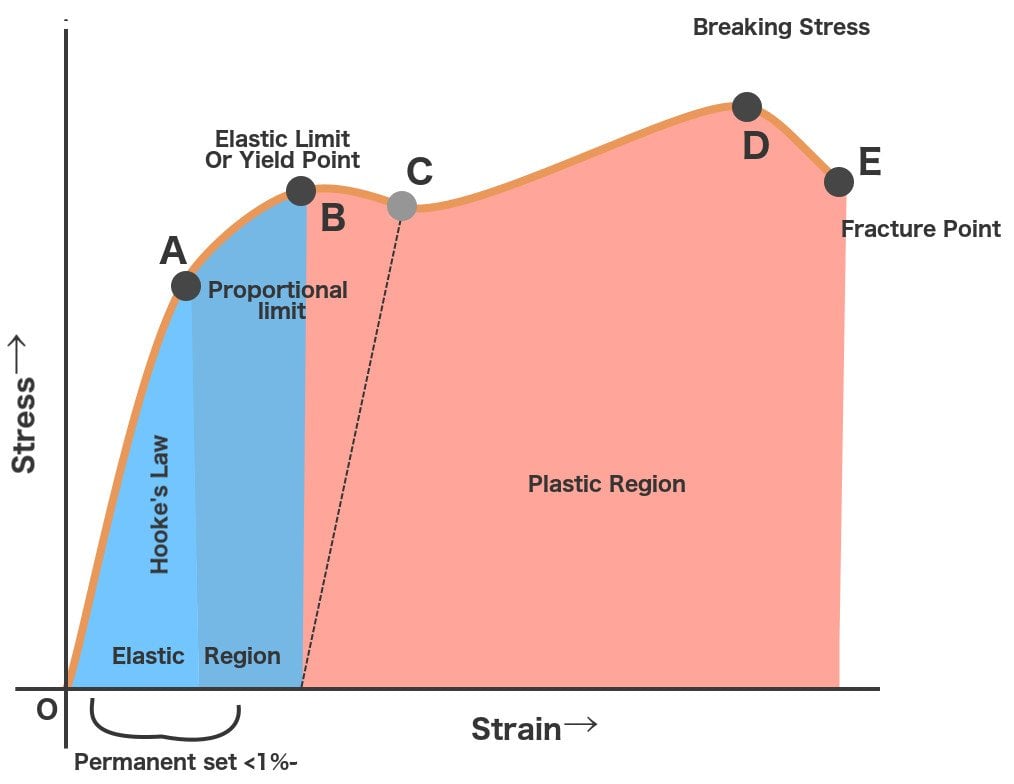
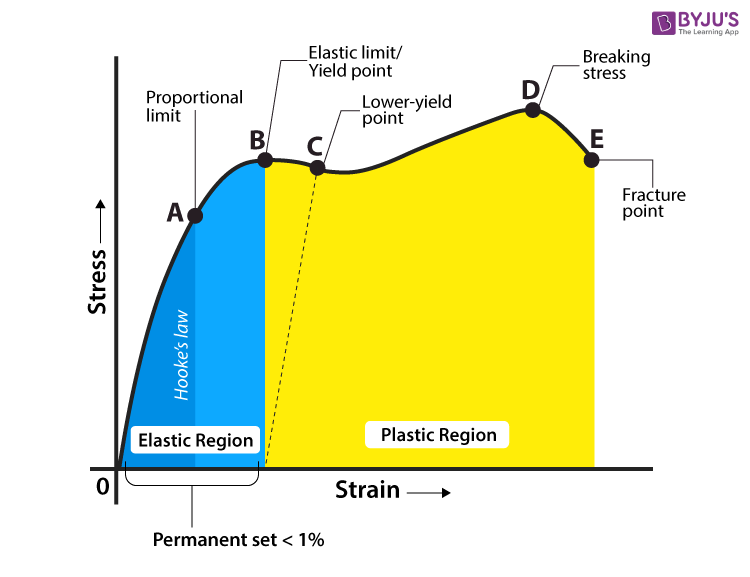
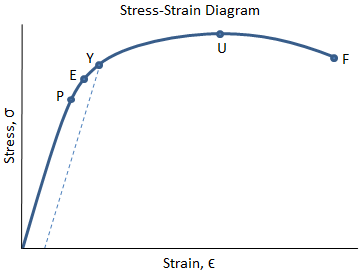
Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Strength (Ultimate stress point) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material have to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stress strain graphFracture or breaking point (i) Proportional Limit It is the region in the stressstrain curve that obeys Hooke's Law In this limit, the ratio of stress with strain gives us proportionality constant known as young's modulus The point OA in the graph is called the proportional limit (ii) Elastic LimitTo illustrate the yield point in a graph the torque is plotted against the time The diagram has usually three typical regions 10 First, the shear stress increases due to deformation as an elastic response


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Strength At Break Tensile
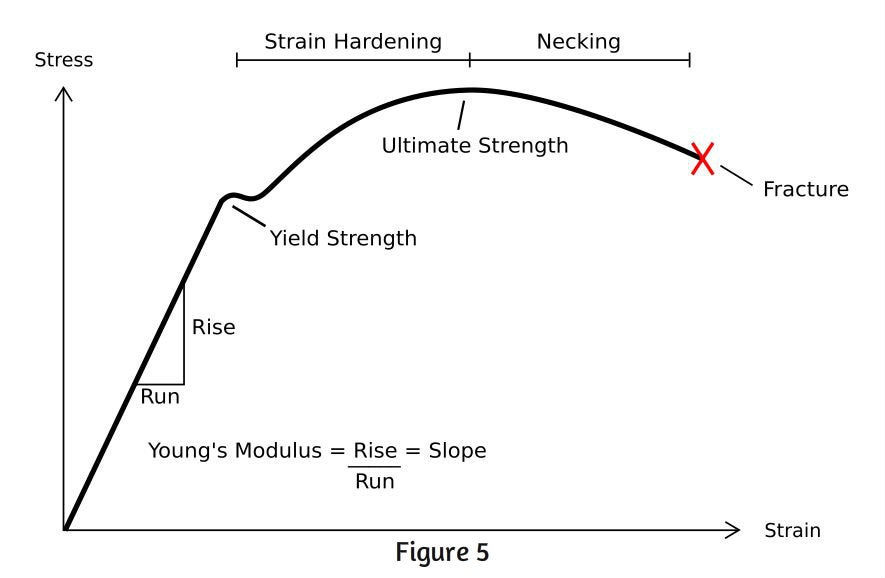
The point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressYield Strength can be seen on a stressstrain curve as the point where the graph is no longer linear Since it is quite difficult to determine an exact point where a line stops being linear, Yield Strength is usually the point where the value on the stressstrain curve is 02% off from what it would be if it was completely linearAt a point when the values of the load at that point this is called yield point When the specimen breaks stop the machine Note the ultimate value of the load Determine the yield strength and tensile strength of load dividing the yield load & ultimate load by cross sectional area of the bar Gauge length = 8 inch



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Materials The Problems With Single Point Data Plastics Technology
The stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the material Some plastics' deformation is linearly elastic and once the maximum strength is attained, the material fractures It is difficult to define an exact yield point for certain materials from the stressstrain curveStrength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofThe point at which a material ceases to be elastic and becomes permanently plastic, the point at which it yields, is called its yield point The magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior


Stress Versus Strain
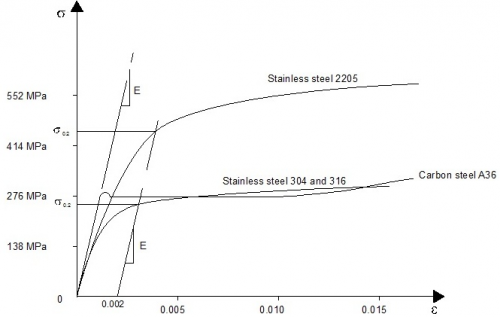


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info
Yield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points and it is upper yield point and lower yield point The stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stressThe yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins2 n Drilling Fluids A parameter of the Bingham plastic modelYP is the yield stress extrapolated to a shear rate of zero (Plastic viscosity, PV, is the other parameter of the Binghamplastic model)A Bingham plastic fluid plots as a straight line on a shear rate (xaxis) versus shear stress (yaxis) plot, in which YP is the zeroshearrate intercept



Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc


Engarc L Offset Yield Method
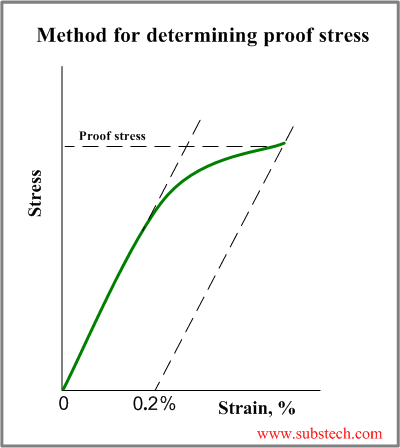
To determine the yield strength using this offset, the point is found on the strain axis (xaxis) of 0002, and then a line parallel to the stressstrain line is drawn This line will intersect the stressstrain line slightly after it begins to curve, and that intersection is defined as the yield strength with a 02% offsetDefinition of yield curve According to Investopedia, the yield curve graphs the relationship between bond yields and bond maturity More specifically, the yield curve captures the perceived risks of bonds with various maturities to bond investors The US Treasury Department issues bonds with maturities ranging from one month to 30 yearsTensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room Temperature



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
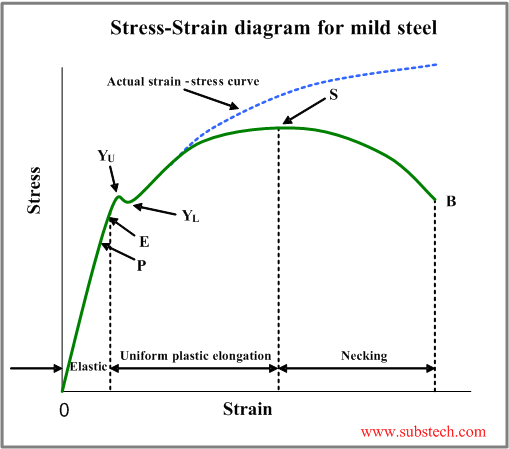
Upper yield point is the maximum load the material requires to initiate plastic deformation Upto this point the dislocations don't need to move but as they cross the point 'B' the elastic limit ends and the dislocations move easing the stress required to cause further strain But again, a lower yield point is present below, and the graph can't travel below thisThe xaxis of the graph of a yield curve is reserved for the time to maturity, while the yield to maturities are located on the yaxis Assume you want to plot the yield curve for the two,We categorize the behavior of materials similar to that of human beings Now, assume that I give you some amount of work to do and keep measuring how much you actually get done As I keep increasing the work load, you will also equally match your



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora
Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material have to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stress strain graph On the graph point U is the ultimate stress point After point U material have very minute or zero strength to face further stressTo determine the yield strength using this offset, the point is found on the strain axis (xaxis) of 0002, and then a line parallel to the stressstrain line is drawn This line will intersect the stressstrain line slightly after it begins to curve, and that intersection is defined as the yield strength with a 02% offsetThe red line is the Yield Curve Increase the "trail length" slider to see how the yield curve developed over the preceding days Click anywhere on the S&P 500 chart to see what the yield curve looked like at that point in time Click and drag your mouse across the S&P 500 chart to see the yield curve change over time



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Imechanica


Yield Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Forums
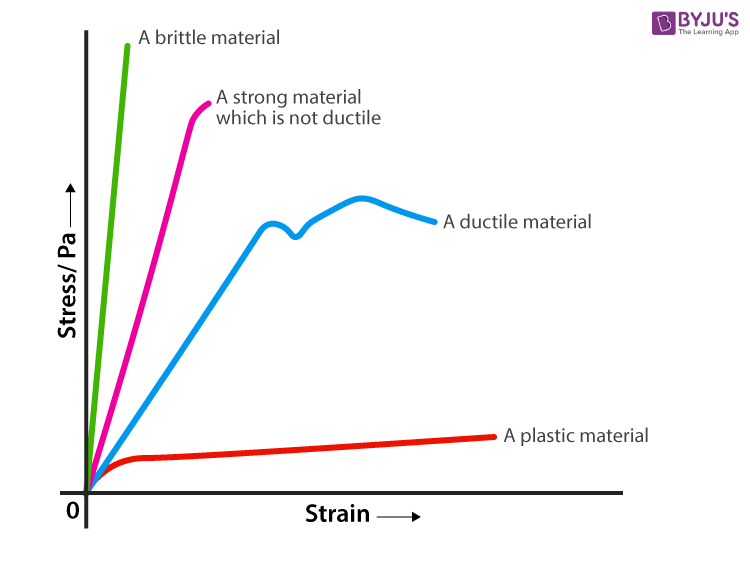
In this ductile material curve, you can see a point labeled yield strength, also known as yield point The dip in the curve at this point is an indication that the material has yielded or deformedDefinition of yield curve According to Investopedia, the yield curve graphs the relationship between bond yields and bond maturity More specifically, the yield curve captures the perceived risks of bonds with various maturities to bond investors The US Treasury Department issues bonds with maturities ranging from one month to 30 yearsData and a data point is taken when the shear rate reaches an equilibrium value Below the yield point, the change in shear rate with stress is extremely small The viscosity remains constant with increasing stress and is referred to as the zero shear viscosity At a given stress, the material starts to flow,



Solved 2 Explain The Engineering Stress And Strain Relat Chegg Com



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora
Different values may be obtained if tangents are drawn at different points Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield pointThe point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressThe effect of Cottrell atmospheres is to increase the yield strength of the material, creating an upper yield point at C in the diagram If the carbon is unable to diffuse as quickly as the dislocations glide, then when point C is reached, the dislocations move away from the carbon and become "unlocked"



How Do You Identify The Elastic Limit And Yield Point On A Stress Strain Graph Physics Stack Exchange


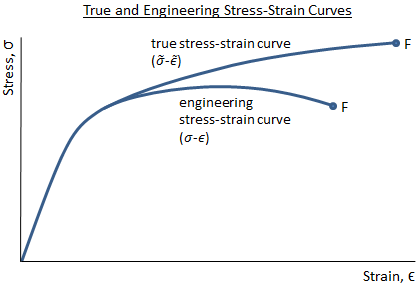
Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve
Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material has to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stressstrain graphQuantifying Yield Points and Limits on Rheology Curves Properties such as yield stress, the onset rate for shear thinning or the limit of linear viscoelasticity are not welldefined values in the same way that viscosity at a defined shear rate can beYield strength is a property often used to describe the stress at which the material begins to function in a plastic manner In the figure, the yield strength is represented by the point of intersection of the parallel line to the stressstrain curve


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora


Q Tbn And9gcsubgeg9vwumror Qhoghyyxdjrgpugf4zei Gvjvgk9mt175y Usqp Cau
Yield strength is a property often used to describe the stress at which the material begins to function in a plastic manner In the figure, the yield strength is represented by the point of intersection of the parallel line to the stressstrain curveIn materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andThe graph above shows the engineering stressstrain curve in blue, the calculated true stress you can convert an engineering stressstrain curve into a true stressstrain curve in the region between the yield point and UTS with the equations References and Further Reading 1 Kalpakjian, Serope and Steven R Schmid (14), Manufacturing



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc



Stress Strain Curve Definition Examples Diagrams
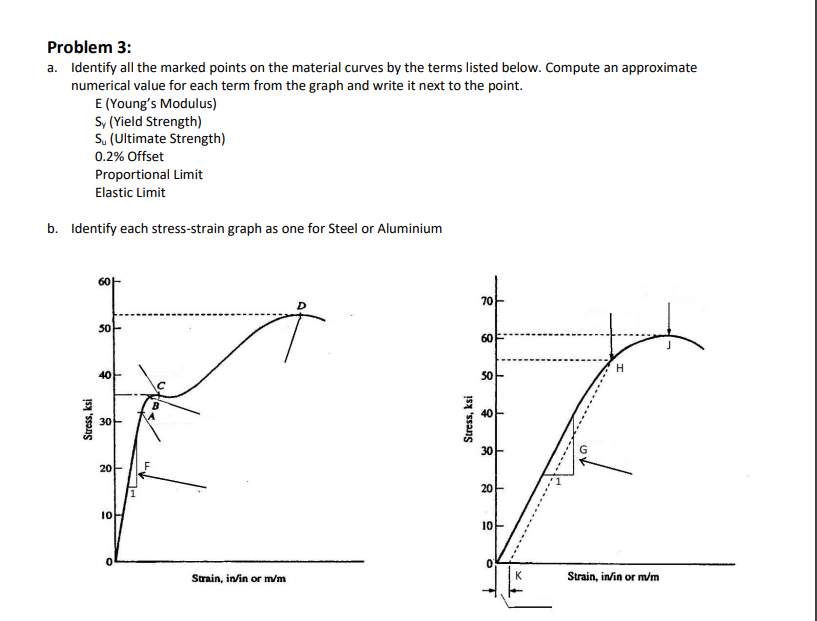
Stress stress diagram construction from test results, finding elastic modulus, yield strength, tensile strength, ductility, resilience and toughness as exactQuestion Can You Please Draw Me A Curve In Graph For This Stress And Strain , And Then Find For Me The Value For The Yield Point , Ultimate Point (U) And The Fracture (R) File Comms Graph Help EX Snap to origin Comms link ON Te TecQuipment 800 700 500 500 400 Stress(MPa) Force (N) 159 300 Edension (m) 0160 0 100 TASK 0 100 002 004



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange


2 3 2 A Sim Tensiletesting 1 Docx
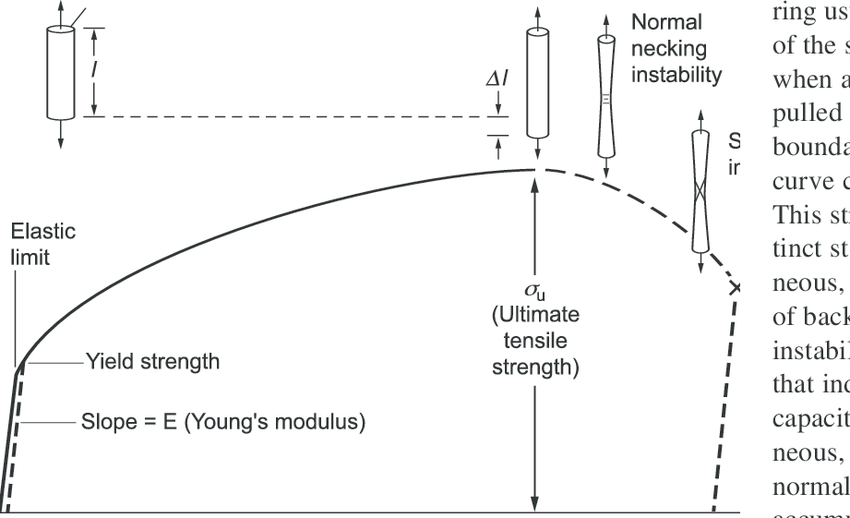


Tensile Stress Strain Curve The Tensile Test Is The Most Common Test Download Scientific Diagram



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
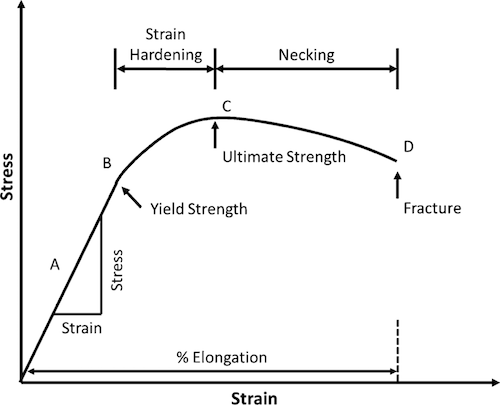


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
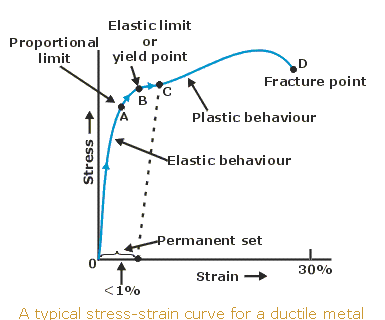


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



Plot Load V S Extension Curve For A Substance On The Graph Show Yield Pointbreaking Pointelastic Limitcrushing Point
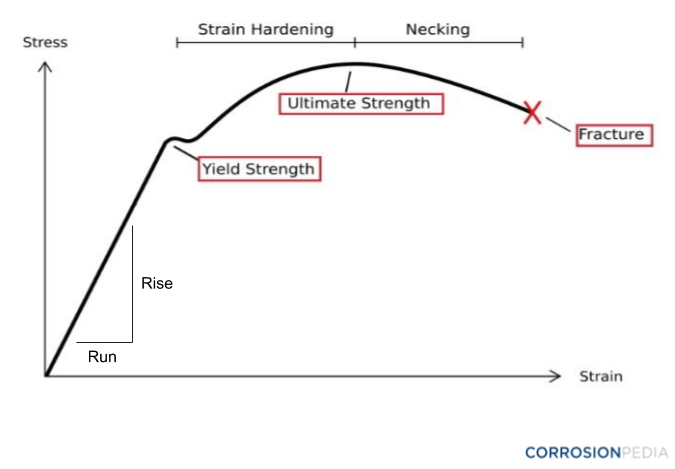


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia


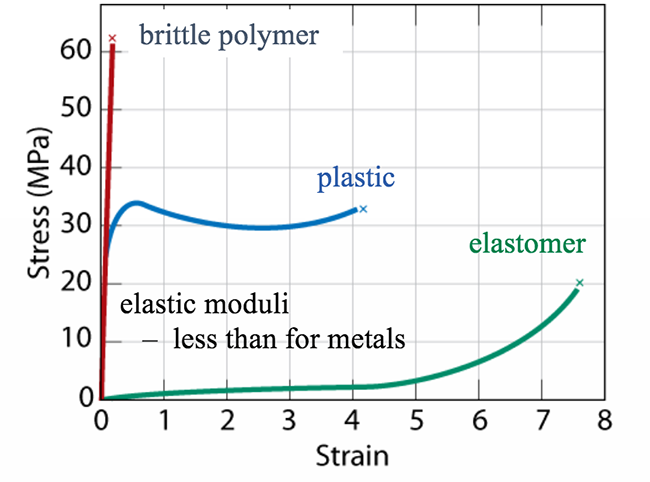
Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Yield Point Definition Curve Elongation General Class Study Com


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


Physics Question New Spec Help The Student Room


Stress Strain And The Stress Strain Curve Materials Science Engineering



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


Solved S Draw A Possible Stress Strain Graph For A Mater Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve Diagram Basic Mechstudies
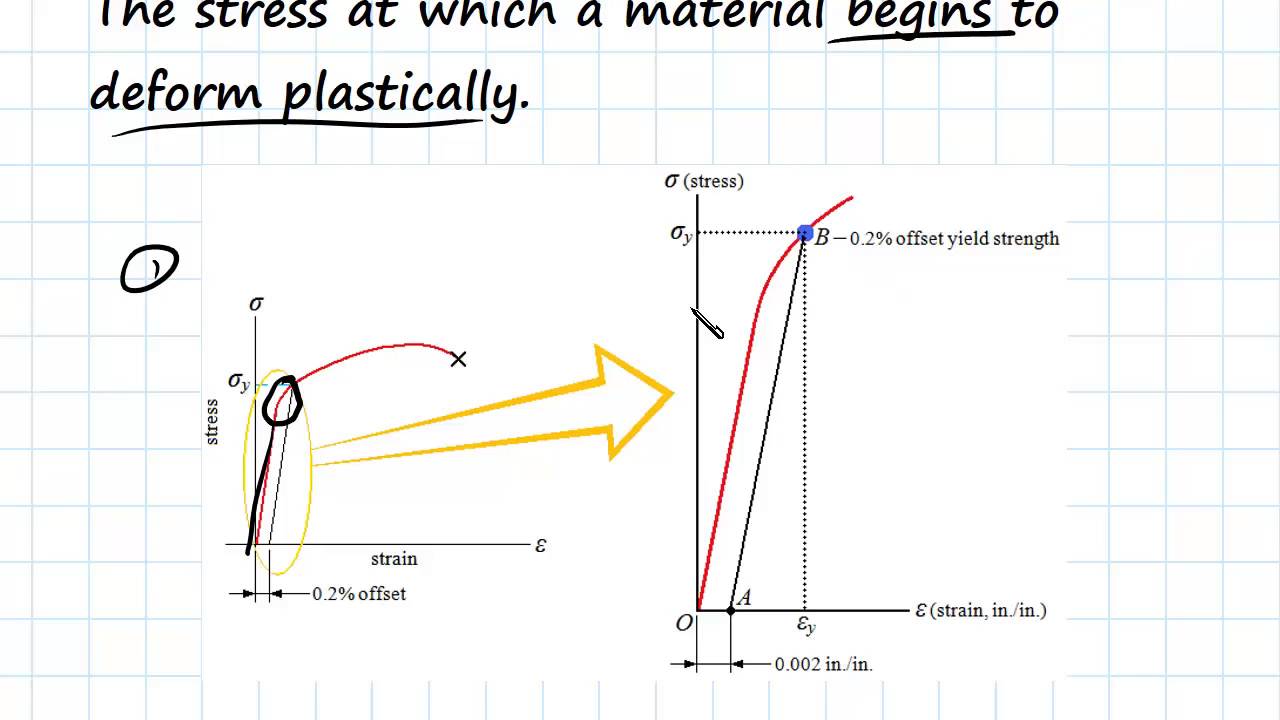


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube
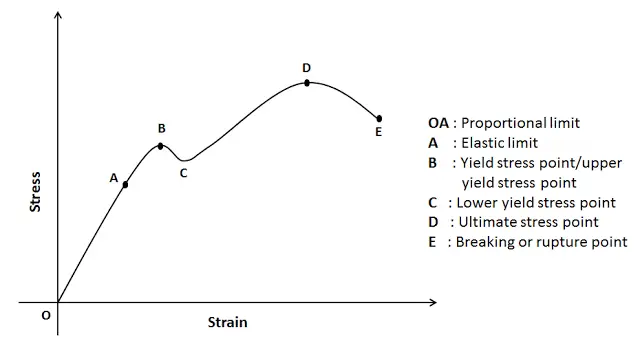


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Strain



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora



Yield Point Instron


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts



Stress Strain Diagram Instron



Yield Strength A Way To Define The Strength Of Materials Andreacollo



Strength At Break Tensile


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Q Tbn And9gcqdhkmo7hherjjmwerev9j1zxqfwpmjetj5gvnkildcbtyau41x Usqp Cau



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Stress Strain Curve Myrank



The Stress Strain Curve Obtained By Loading A Sample Of Compact Bone In Download Scientific Diagram



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion


Solved A Identify All The Marked Points On The Material Chegg Com



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Lecture Notes


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Mechanical Behavior Of Polymers Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
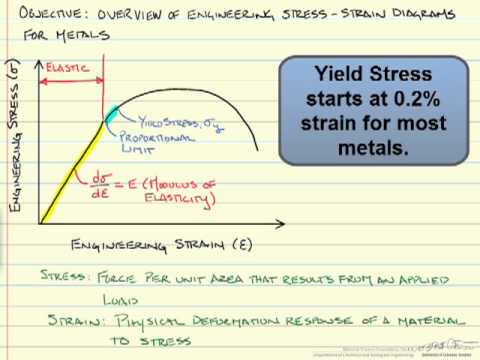


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Permanent Set Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Stack Exchange



Is It Hard To Determine The Elastic Point On A Stress Strain Curve If Yes Why Quora



Explanation Of Stress Strain Curve


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf
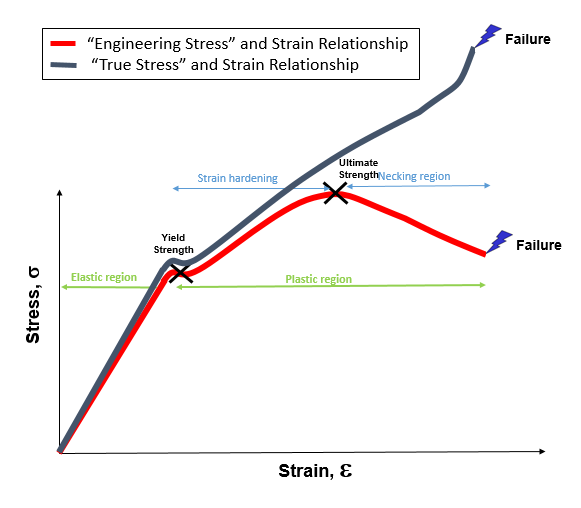


Engineering Stress And Strain Curve Diagram



Physics Complete Sress And Strain Curve
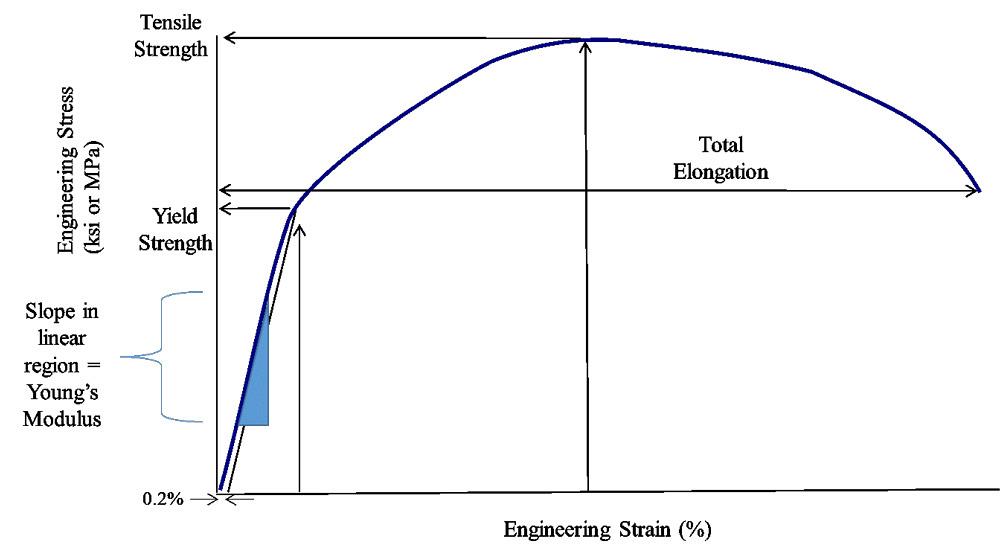


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



Flow Curve And Yield Point Determination With Rotational Viscometry Anton Paar Wiki



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange



Tension Testing Tensile Testing Admet


Engineering Stress Strain Curve


Tensile Testing
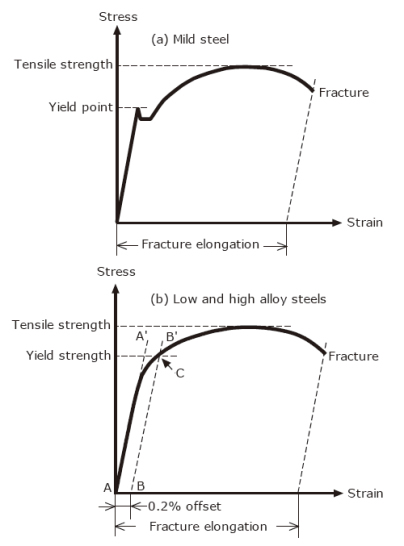


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Q Tbn And9gcq6zmctjndkkjpyak Xrcdf5heom0h Yhbhe5u3bt9reft0h3if Usqp Cau


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
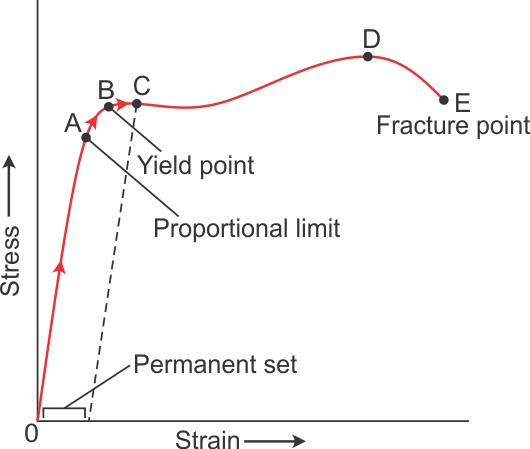


Plot Stress Vs Strain Curve For A Metal On The Graph Depict I Yield Point Ii Fracture Point Iii Proportional Limit Iv Permanent Set Physics Topperlearning Com Ol7k1yrss



What Is Tensile Testing Instron



How Can I Determine The Yield Stress Of A Highly Elastomeric Material That Does Not Exhibit A Turning Point Anywhere On The Stress Strain Curve



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


コメント
コメントを投稿